what kind of reaction is used to make starch and glycogen
Main Deviation – Starch vs Cellulose vs Glycogen
Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are three types of polymeric carbohydrates establish in living cells. Autotrophs produce glucose as the elementary sugar during photosynthesis. All these carbohydrate polymers, starch, cellulose, and glycogen, are made upwards of joining glucose monomer units together past dissimilar types of glycosidic bonds. They serve as chemic energy sources equally well as the structural components of the cell. The main divergence between starch, cellulose and glycogen is that starch is the master storage sugar source in plants whereas cellulose is the main structural component of the cell wall of plants and glycogen is the chief storage carbohydrate energy source of fungi and animals.
This article explores,
1. What is Starch
– Construction, Properties, Source, Function
two. What is Cellulose
– Structure, Properties, Source, Function
3. What is Glycogen
– Structure, Properties, Source, Function
4. What is the difference between Starch Cellulose and Glycogen

What is Starch
Starch is the polysaccharide synthesized by green plants as their main energy store. Glucose is produced by photosynthetic organisms as a simple organic compound. It is converted into insoluble substances like oils, fats, and starch for storage. Insoluble storage substances like starch practise non affect the water potential within the cell. They may not move away from the storage areas. In plants, glucose and starch are converted into structural components like cellulose. They are also converted into proteins which are required for the growth and repair of the cellular structures.
Plants shop glucose in staple foods like fruits, tubers similar potatoes, seeds like rice, wheat, corn, and cassava. Starch occurs in granules called amyloplasts, arranged into semi-crystalline structures. Starch is equanimous of 2 types of polymers: amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a linear and helical chain only amylopectin is a branched concatenation. Around 25% of starch in plants are amylose while the rest is amylopectin. Glucose 1-phosphate is starting time converted into ADP-glucose. Then ADP-glucose is polymerized via i,4-blastoff glycosidic bond by the enzyme, starch synthase. This polymerization forms the linear polymer, amylose. The 1,6-blastoff glycosidic bonds are introduced to the chain by starch branching enzyme that produces amylopectin. Starch granules of rice are shown in effigy ane.

Figure 1: Starch granules in rice
What is Cellulose
Cellulose is the polysaccharide which is fabricated upwardly of hundred to many thousands of glucose units. It is the major component of the prison cell wall of plants. Many algae and oomycetes also apply cellulose to class their cell wall. Cellulose is a direct chain polymer in which 1,4-beta glycosidic bonds are formed betwixt glucose molecules. Hydrogen bonds are formed between multiple hydroxyl groups of 1 chain with neighboring bondage. This allows the two chains to exist held together firmly. Besides, several cellulose chains are involved in the formation of cellulose fibers. A cellulose cobweb, which is made upward of three cellulose chains, is shown in figure 2. Hydrogen bonds between cellulose chains are shown in cyan colour lines.
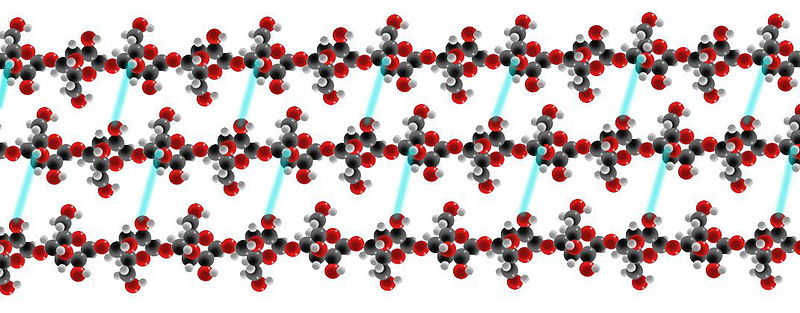
Effigy 2: A cellulose fiber
What is Glycogen
Glycogen is the storage polysaccharide of animals and fungi. Information technology is the analogue to starch in animals. Glycogen is structurally similar to amylopectin but highly branched than the latter. Linear chain forms via one,4-alpha glycosidic bonds and branches occur via ane,6-alpha glycosidic bonds. Branching occurs in every 8 to 12 glucose molecules in the chain. Its granules occur in the cytosol of cells. Liver cells, as well as the musculus cells, store glycogen in humans. One time needed, glycogen is broken down into glucose by glycogen phosphorylase. The process is called glycogenolysis. Glucogon is the hormone which stimulates glycogenolysis. 1,four-alpha glycosidic and 1,half dozen-alpha glycosidic linkages of glycogen are shown in figure 3.
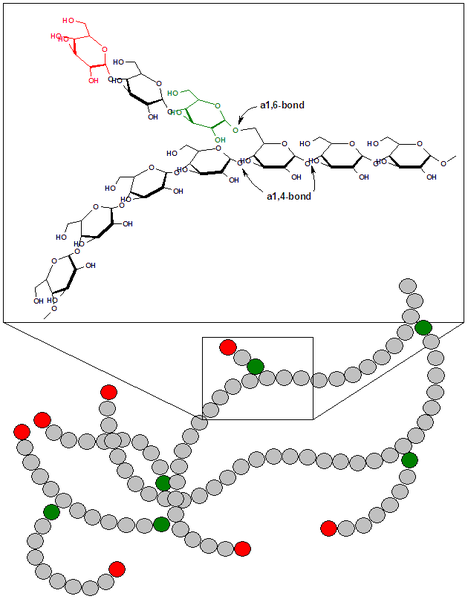
Figure 3: Bonds in glycogen
Divergence Between Starch Cellulose and Glycogen
Definition
Starch:Starch is the main storage sugar source in plants.
Cellulose: Cellulose is the main structural component of the jail cell wall of plants.
Glycogen: Glycogen is the chief storage sugar free energy source of fungi and animals.
Monomer
Starch: The monomer of starch is blastoff glucose.
Cellulose: The monomer of cellulose is beta glucose.
Glycogen: The monomer of glycogen is alpha glucose.
Bail Between Monomers
Starch: The 1,iv glycosidic bonds in amylose and 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bond in amylopectin occur between monomers of starch.
Cellulose: 1,4 glycosidic bonds occur betwixt the monomers of cellulose.
Glycogen: 1,four and i,six glycosidic bonds occur between the monomers of glycogen.
Nature of the Chain
Starch: Amylose is an unbranched, coiled chain and amylopectin is a long branched chain, of which some are coiled.
Cellulose: Cellulose is a straight, long, unbranched chain, which forms H-bonds with adjacent bondage.
Glycogen: Glycogen is a curt, many branched chains of which some chains are coiled.
Molecular Formula
Starch: The molecular formula of starch is (C6H10O5)n
Cellulose: The molecular formula of cellulose is (C6H10O5)n.
Glycogen: The molecular formula of glycogen is C24H42O21.
Molar Mass
Starch: Molar mass of starch is variable.
Cellulose: Molar mass of cellulose is 162.1406 g/mol.
Glycogen: Molar mass of glycogen is 666.5777 g/mol.
Plant in
Starch: Starch can be found in plants.
Cellulose: Cellulose is found in plants.
Glycogen: Glycogen is found in animals and fungi.
Function
Starch: Starch serves as a carbohydrate free energy store.
Cellulose: Cellulose is involved in the edifice of cellular structures like cell walls.
Glycogen: Glycogen serves as a carbohydrate energy store.
Occurrence
Starch: Starch occurs in grains.
Cellulose: Cellulose occurs in fibers.
Glycogen: Glycogen occurs in pocket-size granules.
Conclusion
Starch, cellulose, and glycogen are polysaccharides found in organisms. Starch is found in plants as their major storage form of carbohydrates. Linear bondage of starch are called amylose and when branched they are called amylopectin. Glycogen is similar to amylopectin but is highly branched. It is the major saccharide storage grade in animals and fungi. Cellulose is a linear polysaccharide, which forms hydrogen bonds among several cellulose chains to course a gristly structure. It is the major component of the jail cell wall of plants, some algae, and fungi. Thus, the principal difference between starch cellulose and glycogen is their role in each organism.
Reference:
one. Berg, Jeremy M. "Complex Carbohydrates Are Formed by Linkage of Monosaccharides." Biochemistry. 5th edition. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 01 Jan. 1970. Web. 17 May 2017. <https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK22396/>.
Image Courtesy:
ane. "Rice starch – microscopy" By MKD – Own piece of work (CC By-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
two. "Cellulose spacefilling model"By CeresVesta (talk) (Uploads) – Own work (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia
3. "Glycogen" (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia

Source: https://pediaa.com/difference-between-starch-cellulose-and-glycogen/
0 Response to "what kind of reaction is used to make starch and glycogen"
Post a Comment